Industrial Design Combined with 3D Printing: A Revolutionary Approach to Product Development
Industrial design combined with 3D printing represents a revolutionary approach to product development. This fusion enables the creation of functional, aesthetically appealing, and technically feasible products, taking into account both user needs and manufacturing capabilities. 3D printing brings speed, flexibility, and new possibilities for testing and production into the design process.
What is Industrial Design?
Industrial design is the process of designing products intended for mass production, integrating technical requirements with aesthetic and ergonomic considerations. Its goal is to create objects that not only work well but also appear natural, simple, and intuitive to users. Emphasis is placed on understanding customer behavior, market dynamics, and the environment in which the product will operate.
How 3D Printing is Transforming Industrial Design
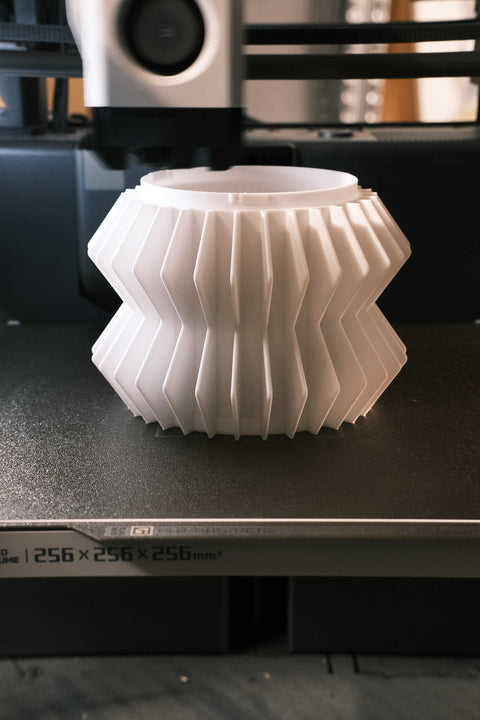
3D printing is changing the way designers approach product development. Instead of relying on traditional prototyping methods, a physical model of a designed object can now be created within a few hours. This enables:
-
Rapid design iterations: Changes can be quickly implemented and tested in real life.
-
Lower prototyping costs: There's no need for expensive molds or tooling.
-
Design freedom beyond traditional manufacturing limits: 3D printing allows for the creation of shapes and structures that would otherwise be unachievable.
Product Design Stages Using 3D Printing
-
Analysis and Brief Definition
The initial stage defines end-user needs and technical possibilities, setting the direction of the development process. -
Creative Phase, Concepts, and Research
Collecting inspiration, analyzing the market, and generating initial ideas through sketches or moodboards. -
Digital Design and Visualization
A CAD model is created, ready for 3D printing. Proportions, ergonomics, and functionality are tested at this stage. -
Prototyping with 3D Printing
Quickly creating a physical model enables immediate feedback and fine-tuning of details. -
Finalization and Production Preparation
Refining surface details, choosing suitable materials, and adapting the design to the selected manufacturing technology.
Benefits of Integrating 3D Printing into Industrial Design
-
Faster product development cycles
-
Opportunities for personalization and small-batch production
-
More sustainable, on-demand manufacturing
-
Easier functionality and ergonomics testing
Conclusion
The combination of industrial design and 3D printing creates ideal conditions for the development of innovative products. Designers can experiment with both form and function without unnecessary compromises, opening new possibilities for startups and established manufacturers alike. This approach also supports more sustainable and efficient production, aligned with the current needs of both the market and society.